This clause describes how ETSI MEC and oneM2M platforms can work together to enable real-time warehouse automation, combining low-latency decision-making with scalable IoT data management. By integrating MEC edge computing with oneM2M’s standardized service layer, warehouses gain the ability to coordinate autonomous systems, monitor environmental conditions, and track assets seamlessly.
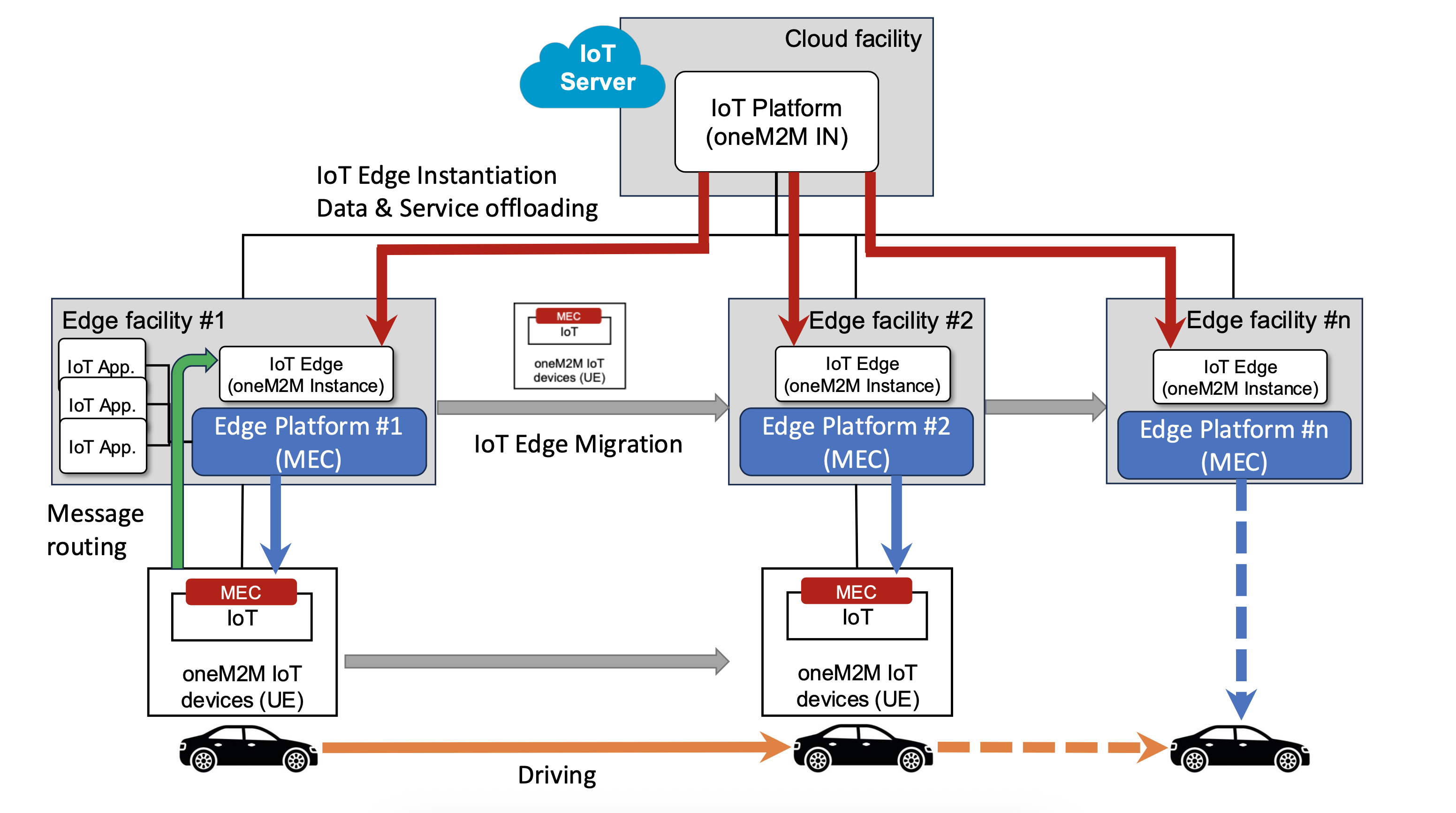
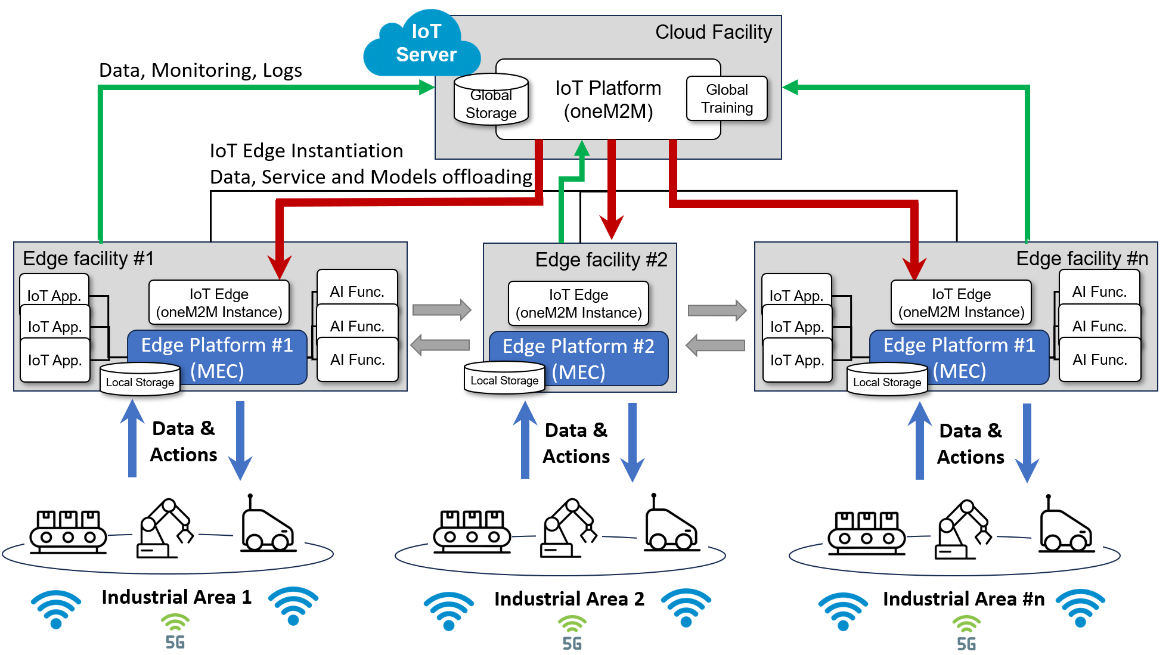
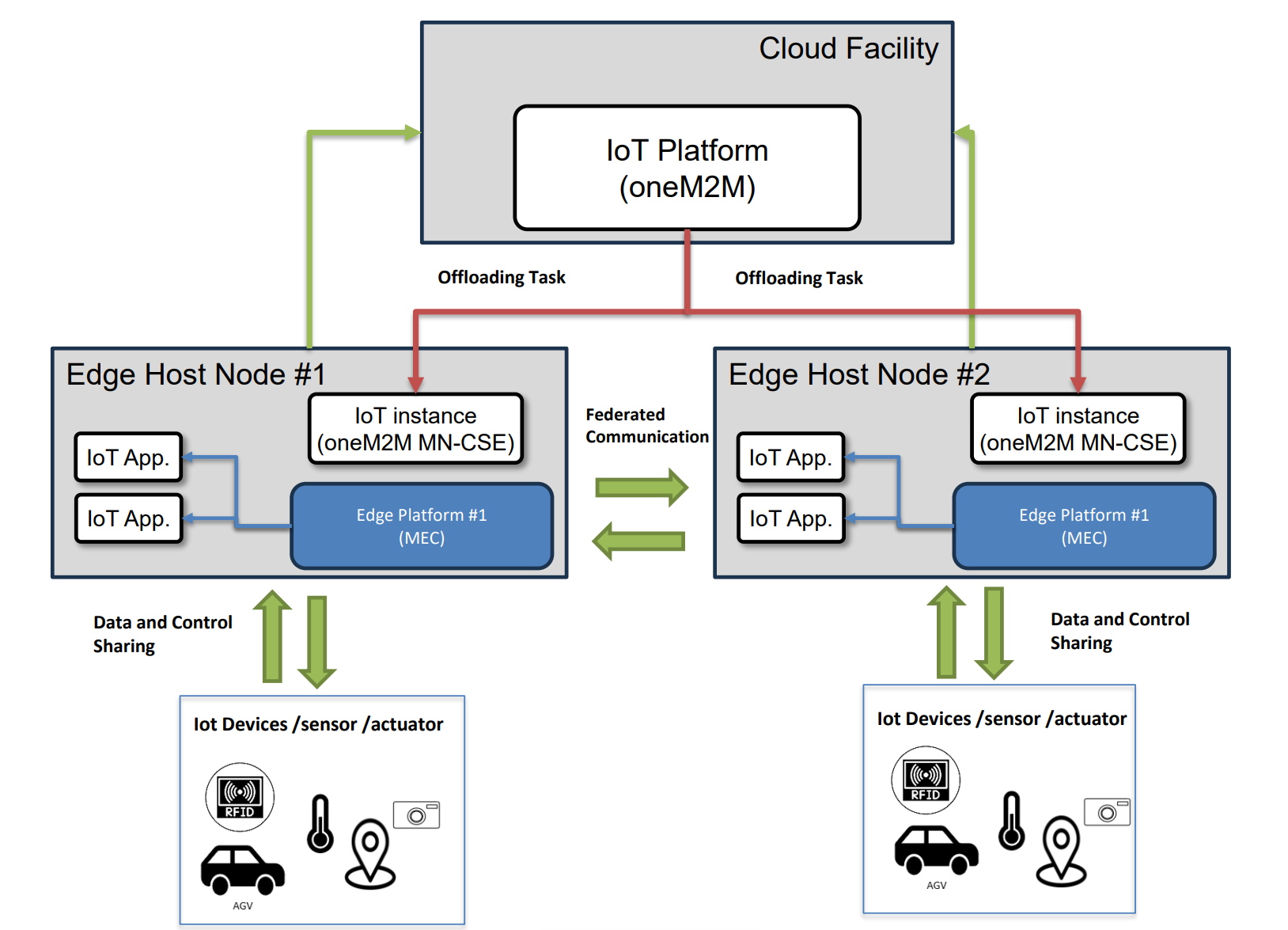
At the core of this architecture, a cloud-based oneM2M IN-CSE acts as the central hub for collecting and managing data from diverse IoT sources, including temperature and humidity sensors, RFID tags, and AGV telemetry systems. The IN-CSE stores this information and orchestrates operations across the warehouse environment.
When time-critical events occur—such as routing autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs), responding to a detected gas leak, or dynamically reallocating inventory—relevant tasks are offloaded to MEC-hosted MN-CSE instances deployed at the edge. These edge nodes provide ultra-low-latency processing, enabling immediate decisions and localized control. For example, the MN-CSE can reroute AGVs around an obstacle, trigger alarms and send notifications to warehouse personnel, or activate air filtration systems in response to hazardous conditions.
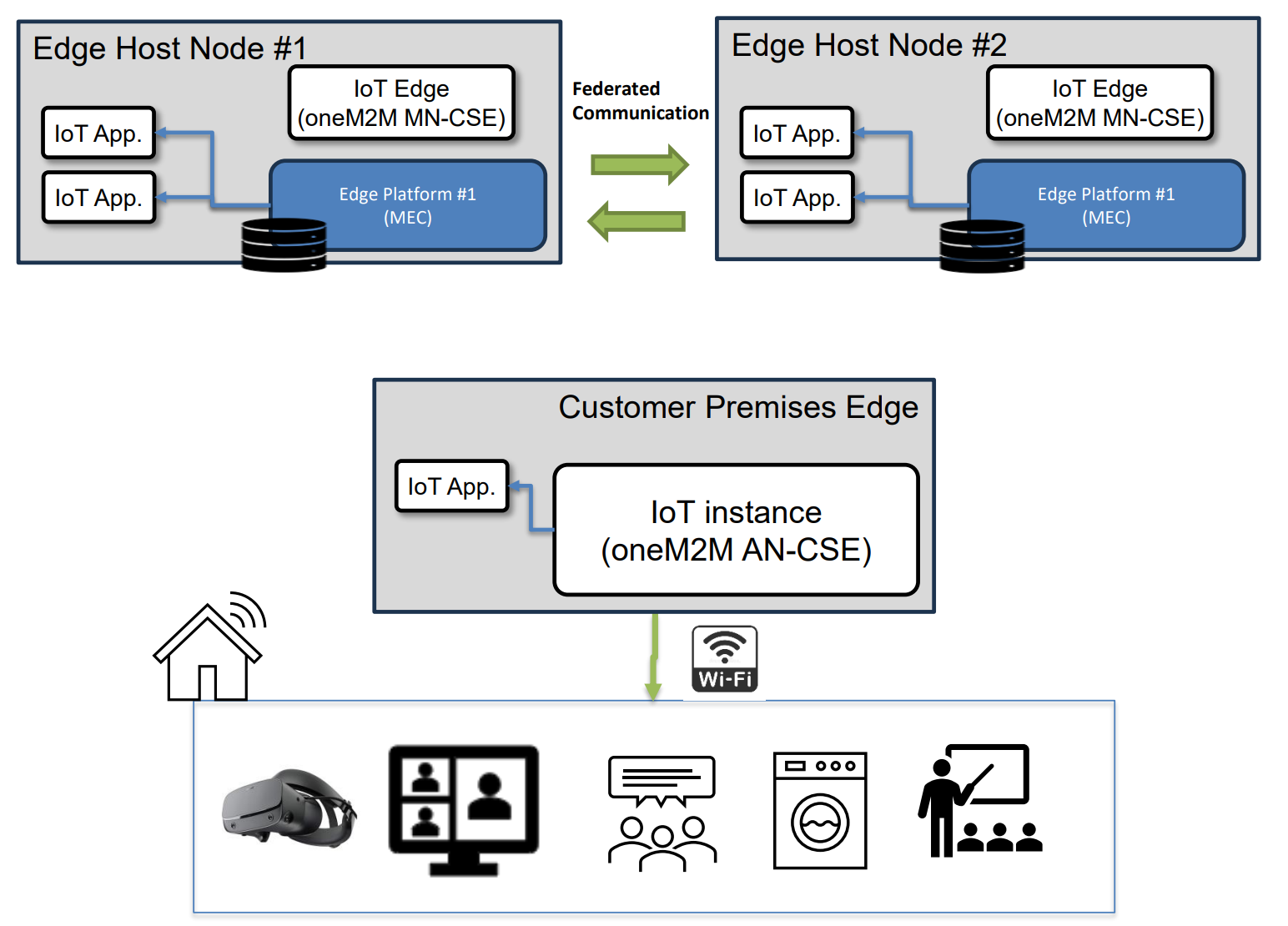
As AGVs and other automated systems operate across expansive facilities, they frequently transition between different MEC coverage zones. The MEC platform ensures service continuity by seamlessly transferring control logic, runtime state, and context data from one edge node to another. This dynamic migration guarantees that automation tasks remain uninterrupted, maintaining both operational efficiency and safety.
Through this architecture, real-time edge analytics complement centralized data management, allowing warehouses to respond dynamically to operational demands while maintaining a unified view of their assets and processes. The combination of oneM2M interoperability and MEC’s low-latency capabilities provides a scalable foundation for future-proof smart warehouse solutions.
Enabling intelligent, resilient, and efficient warehouse automation with MEC and oneM2M.
The founding members of this initiative are CNIT, UNIMORE, xFlow, JK Consulting and Projects, FSCOM, Sejong University, Digital SME, Deutsche Telekom AG, Exacta GSS, Networks SRL, and Telecom Italia S.p.A. To register or learn more, contact estimed@etsi.org or visit https://estimed.etsi.org.
About ETSI
ETSI provides members with an open and inclusive environment to support the development, ratification, and testing of globally applicable standards for ICT systems and services across all sectors of industry and society. We are a non-profit body with more than 950 member organizations worldwide, drawn from 64 countries and five continents. Our members include large and small private companies, research entities, academia, government, and public organizations. ETSI is officially recognized by the EU as a European Standardization Organization (ESO). For more information, visit https://www.etsi.org.